WordPress used to serve just as a blogging software, but according to a WordPress survey, 66% of respondents use WordPress as a Content Management System (CMS). It has developed into a powerful platform over the years. WordPress is much more innovative than plain website building. The growth of WordPress began with new products such as plugins or themes, and now there is so much more. It has become to be known as a popular platform more than anything else. No matter what kind of business you have WordPress has what you need to be able to display your product in the most appealing way.
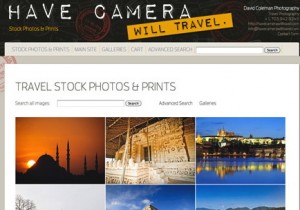 WordPress developers have developed different “plugins” that will cater to your specific needs. One of them is called Photoshelter. It is used for photographers to create a portfolio and website for their business. It is search engine friendly, therefore attracting new clients. It is also used as a selling tool where photographers can even sell prints or downloads. Another WordPress based platform is Tickera which is used for online ticket sales. This is especially great for event organizers because it allows users to buy tickets directly on the site, deliver them digitally, and check-in at the event with their iPhone through the app.
WordPress developers have developed different “plugins” that will cater to your specific needs. One of them is called Photoshelter. It is used for photographers to create a portfolio and website for their business. It is search engine friendly, therefore attracting new clients. It is also used as a selling tool where photographers can even sell prints or downloads. Another WordPress based platform is Tickera which is used for online ticket sales. This is especially great for event organizers because it allows users to buy tickets directly on the site, deliver them digitally, and check-in at the event with their iPhone through the app.
Scribe was created by Copyblogger Media and is a content marketing software. It is basically your own personal writing assistant that uses three simple steps: research, optimize, and connect. It will show you topics and keywords that your audience prefers, analyze your content, and will help to crosslink your content to increase usability and time on site.
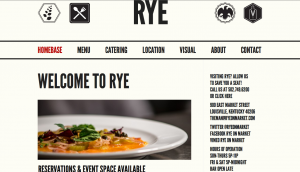 Not only is WordPress great for all types of sites listed above, it can also be used to create beautiful websites to share your wedding on your own website, or share your music with your fans. Also, using a WordPress site for your restaurant allows users to view your location and hours, menu, and even make reservations right from their mobile device like the ones Innovise helped to create for Louisville restaurants Rye and Decca.
Not only is WordPress great for all types of sites listed above, it can also be used to create beautiful websites to share your wedding on your own website, or share your music with your fans. Also, using a WordPress site for your restaurant allows users to view your location and hours, menu, and even make reservations right from their mobile device like the ones Innovise helped to create for Louisville restaurants Rye and Decca.